01 - Modeling Data Management Solutions
Bronze Ingestion Patterns
Ingestion Patterns
- Singleplex: One-to-One mapping of source datasets to bronze tables.
- Multiplex: Many-to-One mapping, i.e. many datasets are mapped to one bronze table.
Singleplex is the traditional ingestion model where each data source or topic is ingested separately. Singleplex usually works well for batch processing.
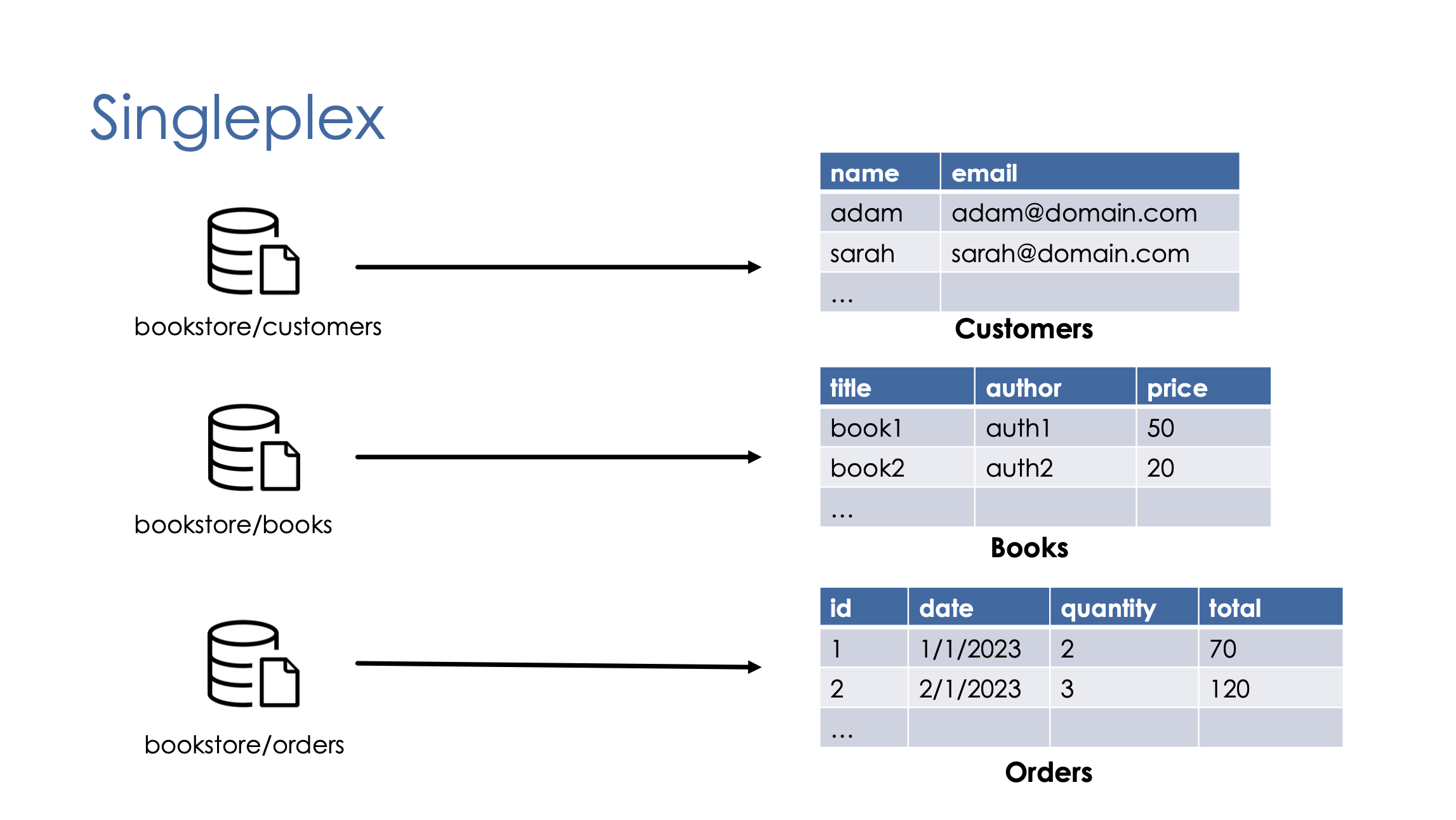
However, for streaming processing of large datasets, if you have many streaming jobs, one per topic, you will hit the maximum limit of concurrent jobs in your workspace.
Multiplex, on the other hand, combines many topics and stream them into a single bronze table. In this model, we typically use a pub/sub system such as Kafka as a source, but we can also use files and cloud objects with Auto Loader.
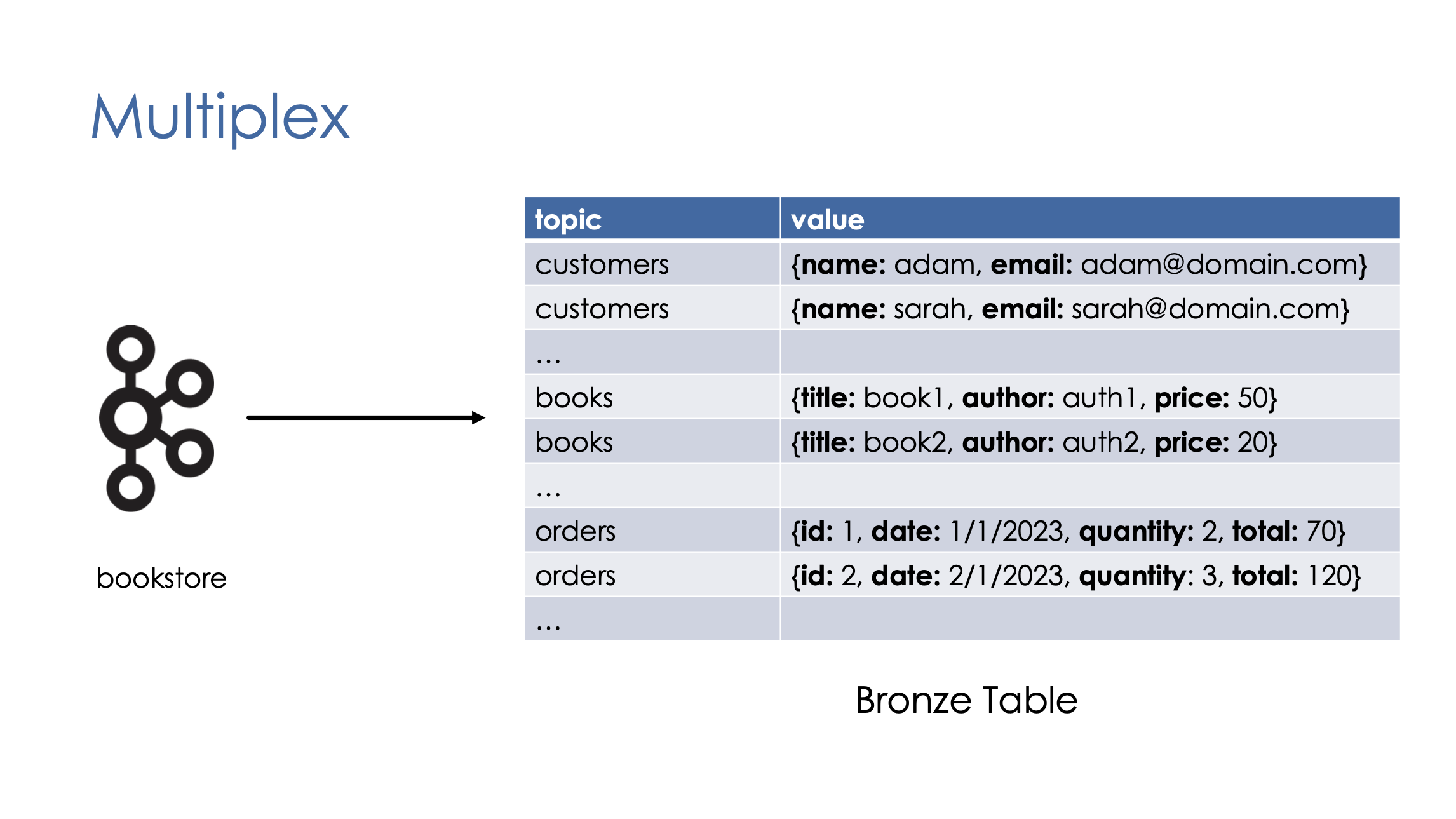
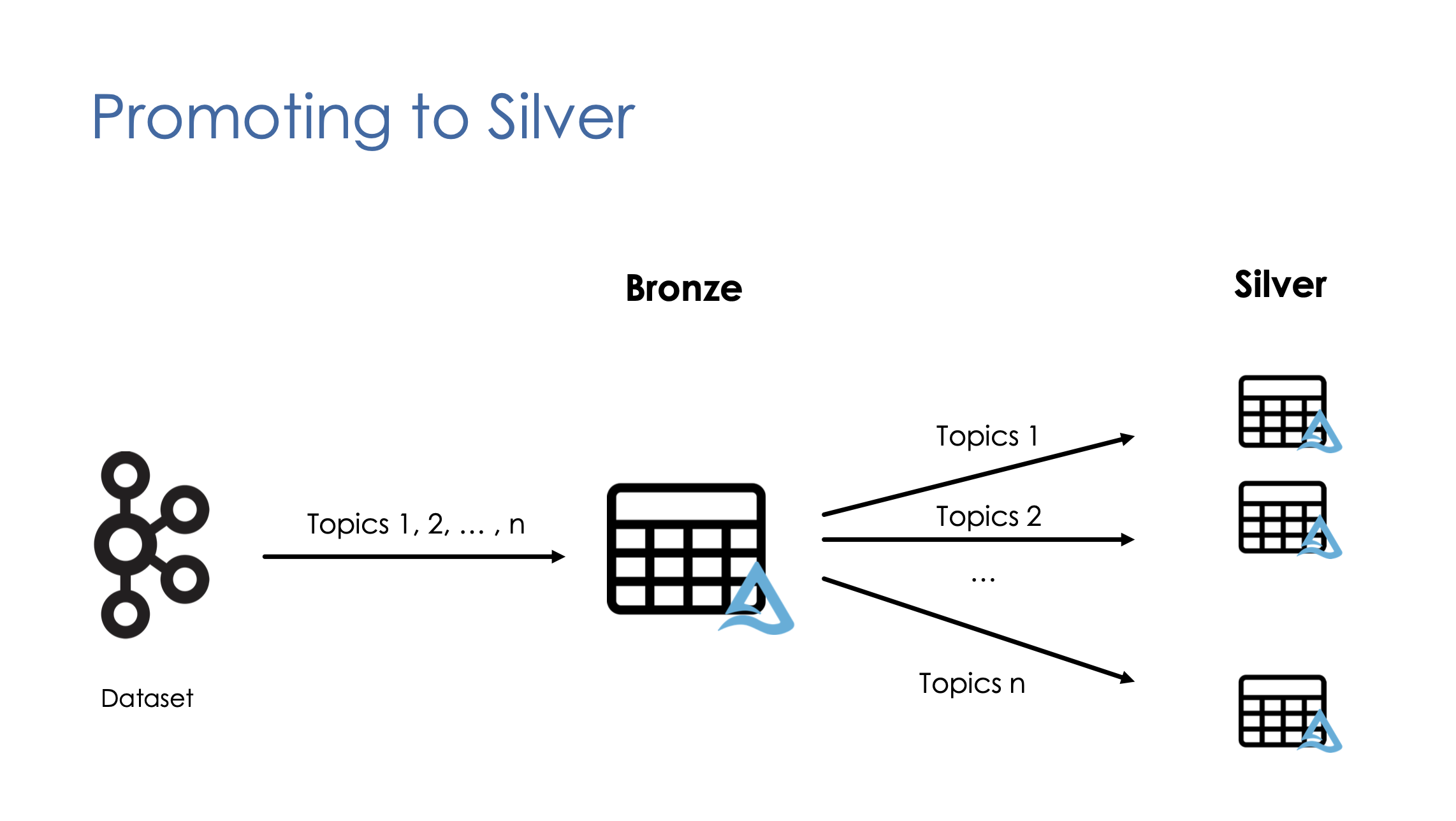
In Multiplex pattern, the records are organised into topics along with the value columns that contains the actual data in JSON format. Later in the pipeline, the multiplex bronze table will be filtered based on the topic column to create the silver layer tables.
Quality Enforcement
| |
Slowly Changing Dimensions (SCD)
Change Data Capture
Delta Lake CDF
Change Data Feed (CDF) is a new feature built-in Delta Lake that allows to automatically generate CDC feeds about Delta Lake tables.
CDF records row-level changes for all the data written into a delta table. These include the raw data along with metadata indicating whether the specified row was inserted, deleted, or updated.
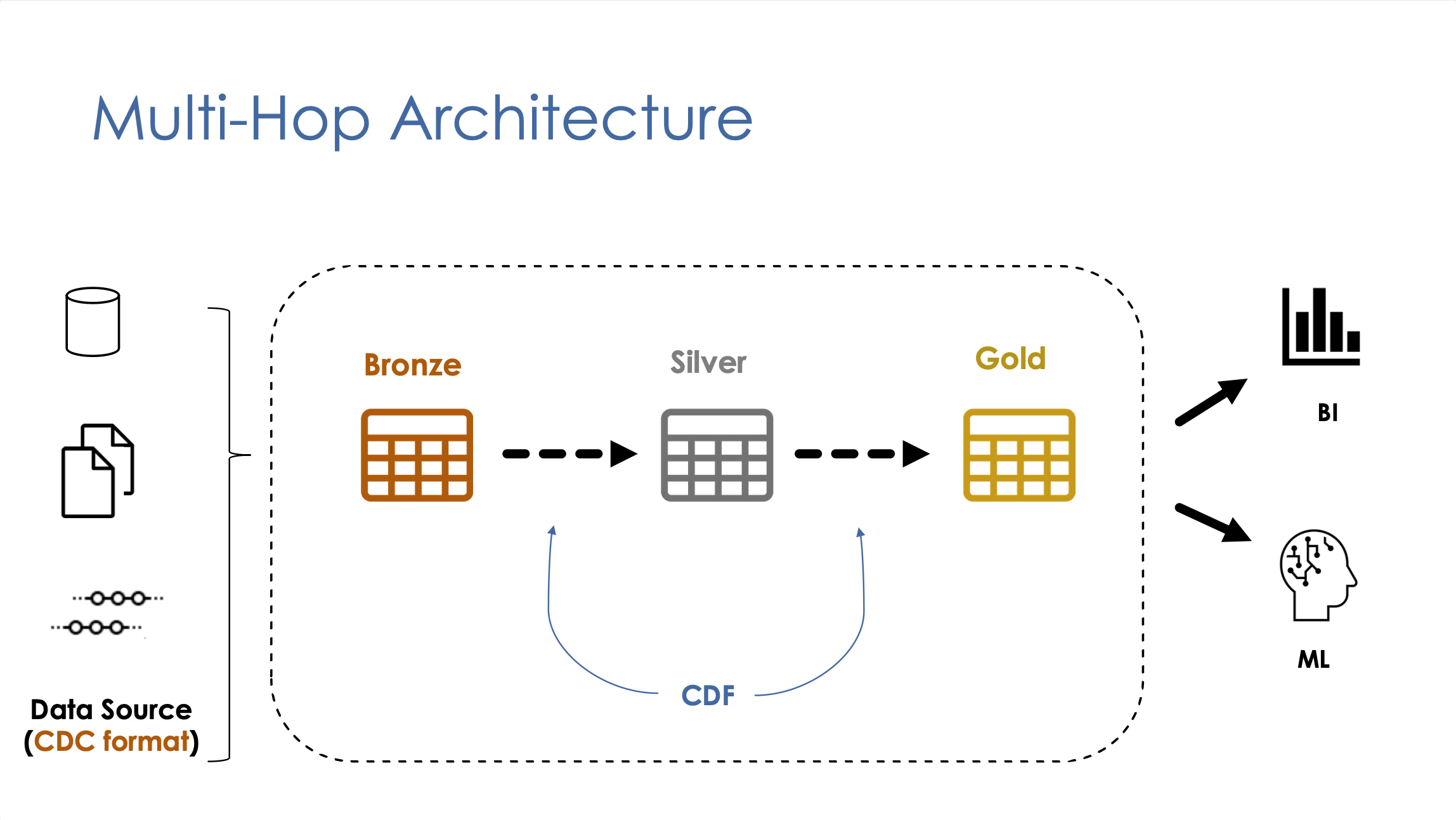 CDF is used to propagate incremental changes to downstream tables in a multi-hop architecture.
CDF is used to propagate incremental changes to downstream tables in a multi-hop architecture.
Query the change data
To query the change data, we can use the follow sql command
| |
Or
| |
Enable CDF
CDF is not been enabled by default, you can enable CDF via following commands
New tables
| |
Existing table
| |
You can also use this spark configuration in your notebook
| |
CDF Retention
- Follow the retention policy of the table.
- When running
VACUUM, CDF data is also deleted.
CDF Usage Scenario
- Use CDF when
- Generally speaking, we use CDF for sending incremental data changes to downstream tables in a multi-hop architecture. These changes should include updates and deletes.
- Use CDF when only a small fraction of records updated in each batch. Such updates usually received from external sources in CDC format.
- Don’t use CDF when
- If these changes are
append-only, then there is no need to use CDF. We can directly stream these changes from the table. - If most of the records in the table are updated or if the table is completely overwritten in each batch.
- If these changes are
Stream-Stream Joins
Stream-Static Joins
Materialised Gold Tables
02 - Databricks Tooling (20%, 12/60)
Databricks Workflow
RESTful API
Databricks CLI
The Databricks CLI is simply a Pytohn wrapper of above RESTful API.
To install the Databricks CLI, you need to run
| |
To configure your Databricks CLI, you need to run
| |
Once you setup your local environment, you can try
03 - Data Processing (30%, 18/60)
04 - Data Modeling (20%, 12/60)
05 - Security & Governance (10%, 6/60)
Propagating Deletes
Delete Requests are also known as Request to be Forgotten. They require deleting user data that represent Personally Identifiable Information (PII), such as name, email of the user.
Dynamics Views
Dynamics views allow identity ACL access control list to be applied to data in a table at the column or row level. So user with sufficient privileges will be able to see all the fields, while restricted users will be shown arbitrary results as defined at view creation.
Column level control
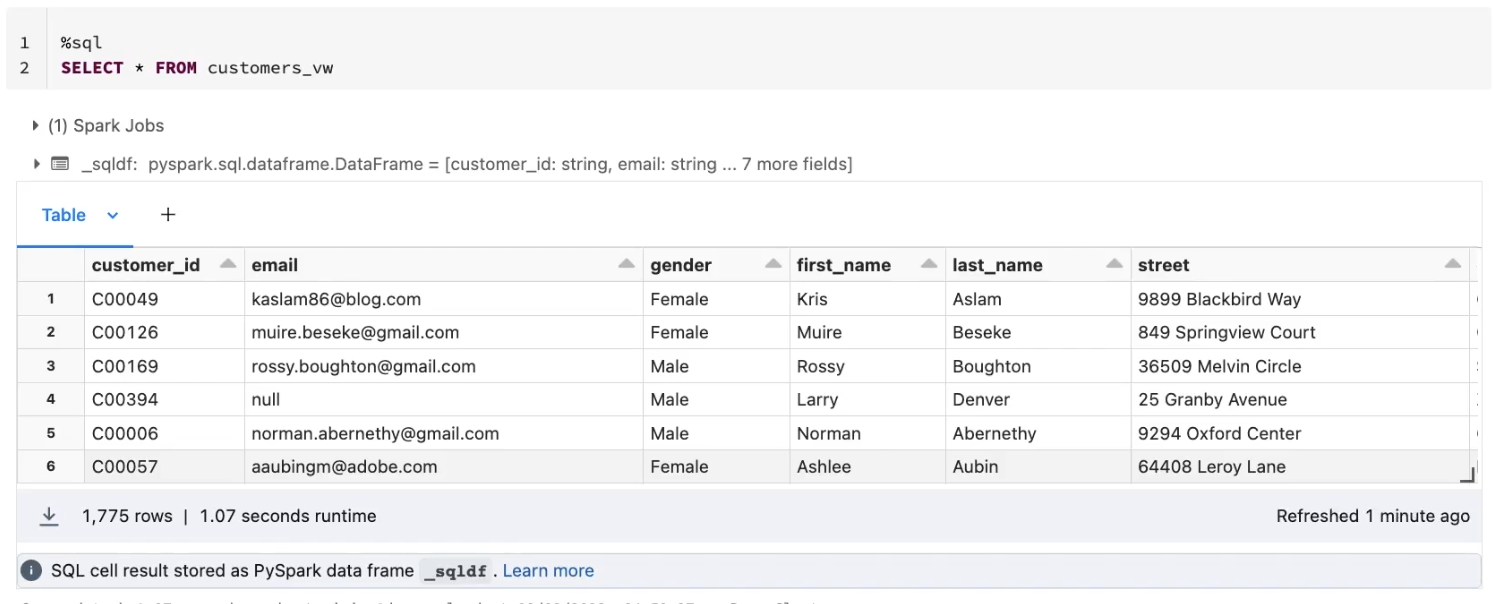
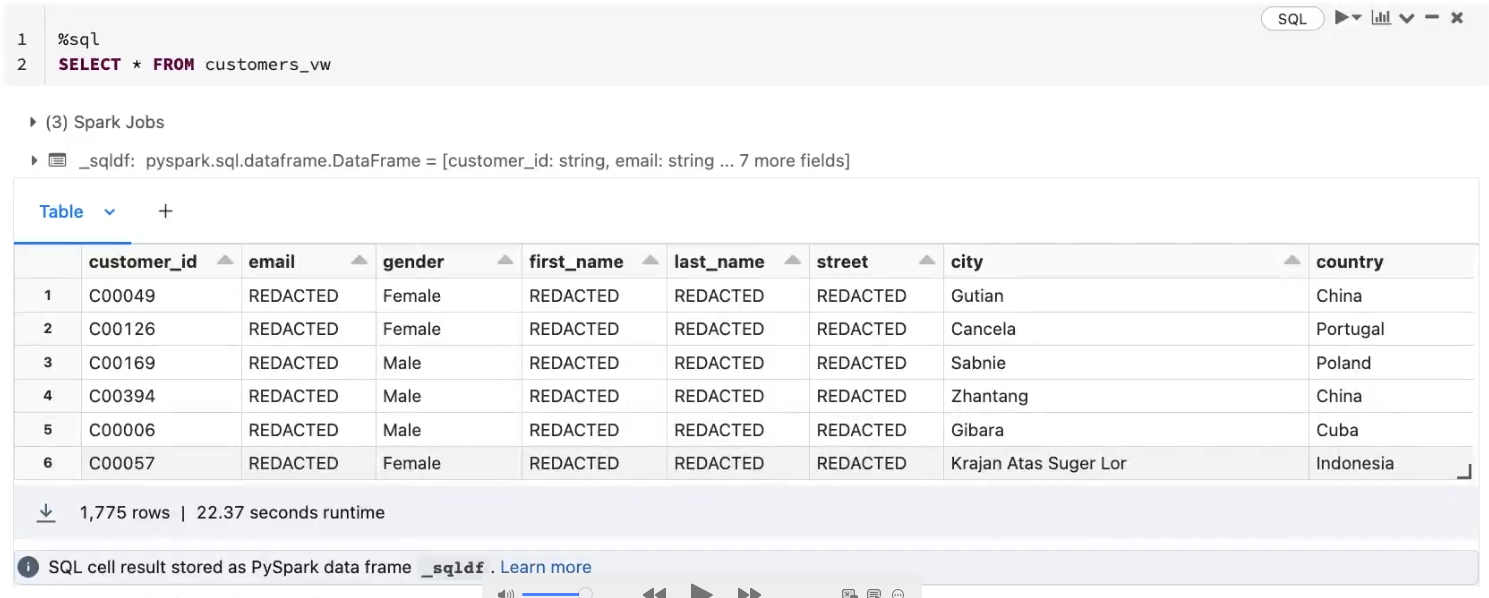
For example, in the following example, only members who are in the admin_demo group have permissions to view PII information, other members will only see redacted results.
| |
For users in admin_demo group,
For other users
Row level control
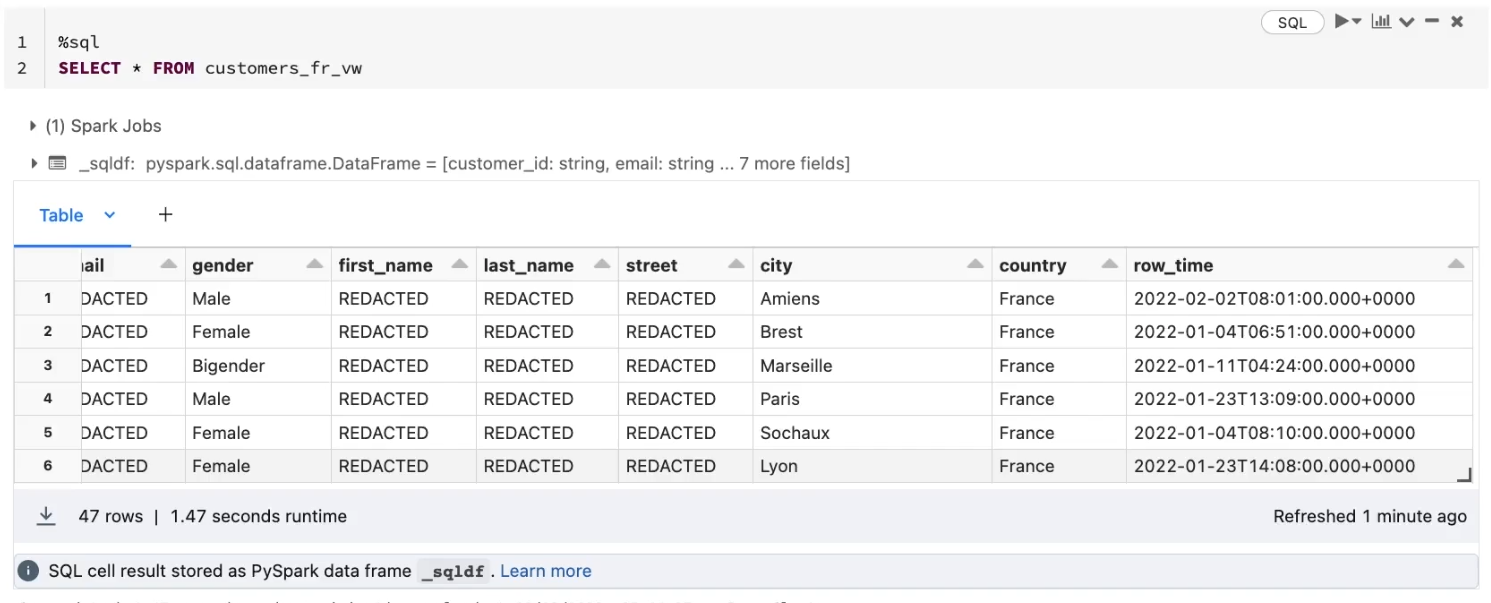
For row level control, we can add WHERE CLAUSE to filter source data on different conditions. Note we can create views on top of another view, and permissions will inherit from previous one.
| |
Here is an example user who is not in the admin_demo group.
06 - Monitoring & Logging (10%, 6/60)
07 - Testing & Deployment (10%, 6/60)
Data Pipeline Testing
- Data Quality test: test the quality of the data
- e.g. You can test that a column
pricehas only values greater than zero. - Apply check
constraintsto Delta tables
- e.g. You can test that a column
- Standard tests: test the code logic
- Unit testing
- Integration testing
- End-to-end testing
Unit Testing
- Approach to testing individual units of code, such as functions
- If you make any changes to them in the future, you can determine whether they still work as you expect them to
- This helps you find problems with your code faster and earlier in hte development lifecycle.
- Use assertion to perform unit test.
- An assertion is a statement that enables you to test the assumptions you have made in your code.
| |
Integration Testing
- Approach to testing the interaction between subsystems of an application.
- Software modules are integrated logically and tested as a group.
End-to-end Testing
- Approach to ensure that your application can run properly under real-world scenarios
- Simulate a user experience from start to finish